Changing the default SSH port on a CentOS system can help enhance and security of your server. By default, SSH runs on port 22.
Step 1: Edit the SSH Configuration File
Open the SSH daemon configuration file with a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Step 2: Change the SSH Port
Look for the line that says:
#Port 22
Uncomment it (remove the #) and change 22 to your desired port number (e.g., 3389):
Port 3389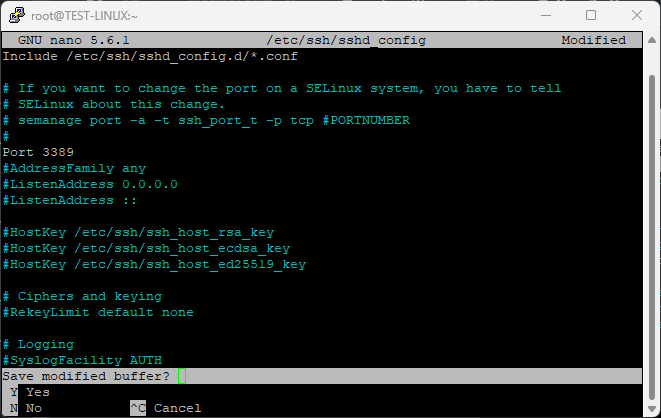
Note: Please choose a port number greater than 1024 to avoid conflicts with well-known services, and less than 65535.
Step 3: Allow the New SSH Port in the Firewall
Update your firewall rules to allow traffic on the new port. For CentOS 7, 8, or CentOS Stream (using firewalls):
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3389/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload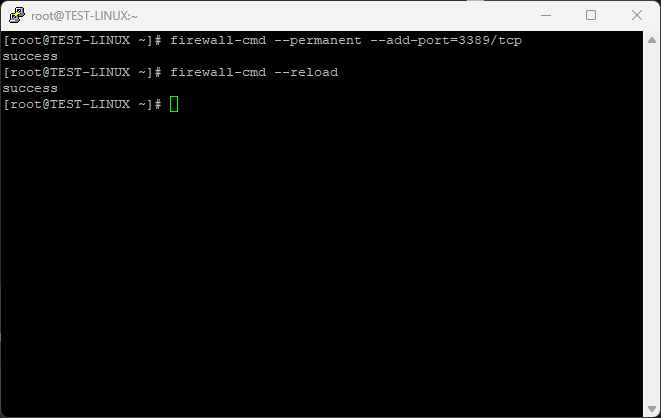
If you’re using iptables instead of firewalld, use:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3389 -j ACCEPT sudo service iptables save
Step 4: Restart the SSH Service
After updating the configuration file, restart the SSH service to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart sshd





